Geomembrana Geotextil: Key Components in Modern Civil Engineering

In modern civil and environmental engineering, the use of synthetic materials to reinforce, separate, filter, and waterproof has revolutionized construction practices. Two of the most widely used materials are geomembrana and geotextil. When combined in a system geomembrana geotextil provides unmatched functionality, especially in projects involving water containment, soil stabilization, and environmental protection.
This article explores the purpose, properties, applications, and combined benefits of geomembrane and geotextile materials in infrastructure development.
What Is a Geomembrana?
A geomembrana (geomembrane in English) is a low-permeability synthetic liner or barrier typically made from polymers such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or polypropylene (PP). Its primary function is to prevent the migration of fluids or gases.
These membranes are commonly used in:
- Landfill liners
- Mining ponds
- Water reservoirs
- Wastewater treatment plants
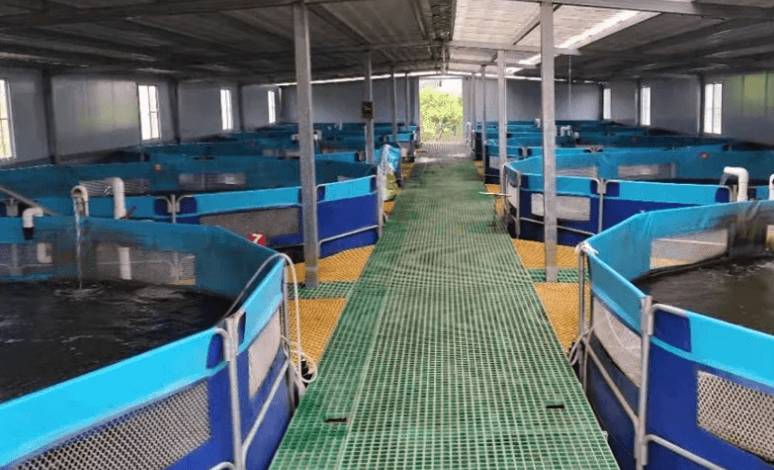
- Aquaculture ponds
Geomembranes are known for their excellent chemical resistance, durability, and UV protection, which make them suitable for harsh environmental conditions.
See also: Innovative technology enhances sushi service operations
What Is a Geotextil?
A geotextil (geotextile in English) is a permeable fabric used in conjunction with soil to improve its engineering propertiesWoven geotextiles: Made by weaving fibers together for strength and load distribution.
- Non-woven geotextiles: Manufactured by bonding fibers using heat or chemicals, ideal for filtration and separation.
Common uses include:
- Road construction
- Erosion control
- Drainage systems
- Railway subgrades
- Retaining wall reinforcement
Combining Geomembrana Geotextil: A Powerful Duo
The geomembrana geotextil combination provides a multi-functional system used in projects where waterproofing, reinforcement, separation, or filtration is required. These two materials are often installed together to enhance performance and durability.
Typical configurations include:
- A geotextile layer placed below a geomembrane to protect it from punctures by sharp objects in the subgrade.
- A geotextile above a geomembrane to prevent abrasion from overlying materials such as gravel or soil.
- Sandwich configurations, where geomembrane is placed between two geotextile layers for protection on both sides.
This synergy provides an effective, long-lasting solution in containment and stabilization projects.
Key Applications of Geomembrana Geotextil Systems
1. Landfill Liners and Covers
In landfills, geomembrana acts as an impermeable barrier to prevent leachate from contaminating groundwater. Geotextil protects the membrane and assists in drainage and separation. Together, they ensure long-term environmental protection.
2. Mining and Heap Leach Pads
Mining operations require robust liners to contain chemical-laden liquids. Geomembranes prevent leakage, while geotextiles cushion the membrane and promote proper fluid flow.
3. Ponds and Reservoirs
Water containment is a major application. Geomembranes keep water from seeping into the ground, and geotextiles stabilize the soil and prevent liner damage from rocks or plant roots.
4. Wastewater Treatment Facilities
The geotextile prevents soil infiltration, and the geomembrane ensures fluid retention.
5. Canal Linings
To prevent seepage loss in irrigation systems, geomembranes line canals while geotextiles protect the liner from mechanical damage and erosion.
Advantages of Geomembrana Geotextil Systems
✅ Enhanced Durability
When used together, geotextiles significantly increase the life of geomembranes by reducing mechanical damage from rocks or construction equipment.
✅ Improved Water Management
Geomembranes block water flow, and geotextiles help manage drainage, allowing for smart water control in civil and agricultural settings.
✅ Eco-Friendly Solution
These materials reduce soil erosion, groundwater contamination, and land degradation, supporting sustainable engineering practices.
✅ Adaptability to Harsh Conditions
Geomembrana geotextil systems are chemically resistant and UV-stable, allowing installation in extreme environments like deserts, chemical plants, or wastewater zones.
Choosing the Right Materials
Project success depends on selecting the appropriate type and thickness of geomembrana and the right class of geotextil. Factors to consider:
- Soil type and structure
- Load intensity and traffic
- Presence of sharp objects or roots
- Chemical exposure risk
- Project life expectancy
For example, HDPE geomembranes offer superior chemical resistance and are commonly used in landfills, while LLDPE is more flexible for undulating terrains.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation is crucial to performance. A typical process includes:
- Surface Preparation: Remove sharp stones and vegetation.
- Geotextil Layer Installation: Laid first to create a cushion and provide separation.
- Geomembrana Deployment: Rolled out over the geotextile, often with overlapping seams.
- Seaming: Use heat welding or chemical adhesives to ensure watertight seals.
- Backfilling: A protective soil or gravel layer is added on top.
Inspections, testing, and quality control are performed throughout to guarantee integrity.
Innovations in Geosynthetics
Technological advancements have made geomembrana geotextil systems more efficient and environmentally friendly:
- Textured geomembranes improve friction for better adherence to slopes.
- Smart monitoring tools embedded in liners can detect leaks or movement in real time.
These innovations are redefining infrastructure durability and safety standards.
Real-World Case Study: Agricultural Reservoir in Mexico
Engineers implemented a geomembrana geotextil solution using a 1.5 mm HDPE liner over non-woven geotextile fabric. The result:
- Water retention improved by over 95%
- Reduced operational costs due to lower water replenishment
- The project achieved a 20-year design life with minimal maintenance
Conclusion
Their ability to work together to provide reinforcement, protection, separation, filtration, and containment makes them indispensable in today’s engineering landscape.
From landfills and canals to reservoirs and roads, this dynamic duo ensures long-lasting infrastructure, reduces environmental risk, and promotes sustainability. As demand for resilient infrastructure increases, integrating geomembrane and geotextile systems will remain a best practice for forward-thinking engineers and project managers.