HWhat Role Does Sleep Play in Blood Pressure Levels?

Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular health, particularly in regulating blood pressure levels. The body’s processes during rest are essential for recovery and equilibrium, and sleep disruptions can lead to severe health consequences, including hypertension. Sleep is not just a time for rest—it’s an active period when the body engages in vital maintenance and regulation, impacting everything from hormone levels to vascular health. For those monitoring their health closely, understanding the connection between sleep and blood pressure can help optimize personal habits and improve outcomes. This is especially important as modern tools like smartwatches and health apps make it easier to track these patterns
How Sleep Regulates Blood Pressure
The Role of Sleep in Lowering Nighttime Blood Pressure
During sleep, blood pressure naturally dips in a process called nocturnal dipping, which allows the cardiovascular system to recover from daytime activity. This reduction is essential for maintaining healthy vascular function and preventing undue strain on the heart and blood vessels. However, when sleep is disrupted, this dip may not occur, increasing the risk of cardiovascular issues. For example, individuals using advanced wearable technology like the HUAWEI Watch D2 can observe how their blood pressure behaves even during rest. These devices provide 24-hour monitoring, delivering real-time data on systolic and diastolic pressures, pulse rate, and overall trends. Such insights empower users to see how effectively their body recovers at night and whether adjustments are needed to optimize their sleep routines.
Circadian Rhythms and Blood Pressure Regulation
The body’s internal clock, or circadian rhythm, is a powerful force in regulating blood pressure. This natural cycle governs the rise and fall of blood pressure levels throughout the day, including the crucial nighttime dip. Misalignments in this rhythm, caused by irregular sleep schedules or shift work, can disrupt blood pressure regulation and contribute to chronic conditions. For example, health apps can help users identify optimal times for sleep and wakefulness, offering suggestions to align habits with the body’s natural rhythms. Knowing when is the best time to take your blood pressure—usually in the morning before eating or in the evening—further enhances understanding and management of these cycles.
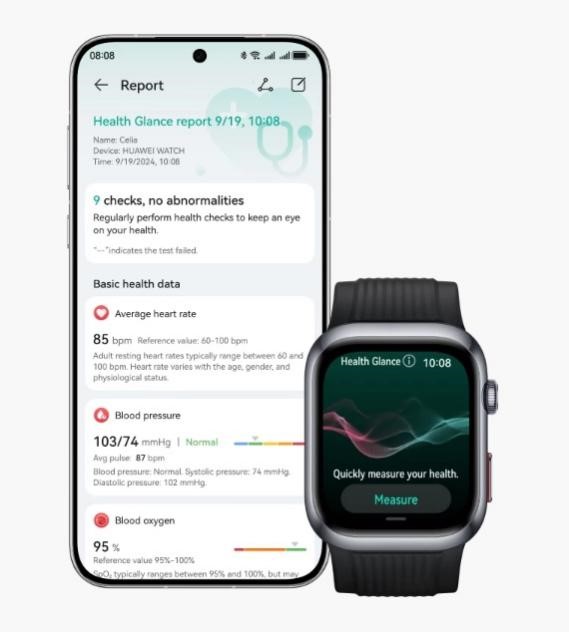
Effects of Poor Sleep on Blood Pressure Levels
Increased Risk of Hypertension Due to Sleep Deprivation
Chronic sleep deprivation is a significant risk factor for hypertension. Insufficient sleep increases stress hormones like cortisol, which raise blood pressure levels. Additionally, the body’s ability to regulate sodium and water balance is impaired, further exacerbating hypertension risks. For instance, consider an individual juggling a demanding job and poor sleep patterns. Their wearable health device may record consistent elevations in blood pressure during stressful weeks. This data could prompt them to prioritize relaxation techniques and earlier bedtimes, mitigating these negative effects over time.
Sleep Disorders and Their Impact on Blood Pressure
Sleep disorders such as sleep apnea significantly influence blood pressure levels. Sleep apnea, characterized by repeated breathing interruptions during sleep, can cause spikes in blood pressure due to oxygen deprivation. These nightly disturbances often lead to sustained hypertension if left untreated. Monitoring tools integrated with health apps can help detect irregularities like abnormal breathing patterns. Early identification through comprehensive reports allows users to seek medical advice and make lifestyle changes to improve sleep quality and cardiovascular health.
The Importance of Deep Sleep and Sleep Quality
REM and Non-REM Sleep in Blood Pressure Control
Both REM (rapid eye movement) and non-REM sleep play essential roles in regulating blood pressure. Non-REM sleep is particularly restorative, aiding in the repair of blood vessels and reducing heart rate. REM sleep, associated with vivid dreaming, is vital for maintaining a healthy balance of hormones that influence blood pressure. The interplay between these sleep stages underscores the importance of achieving a full sleep cycle. Tracking sleep quality through wearable devices provides a clear picture of whether an individual is getting sufficient REM and non-REM sleep. By reviewing detailed data, users can identify disruptions and adjust their habits for better outcomes.
The Link Between Sleep Duration and Cardiovascular Health
Sleep duration is directly linked to cardiovascular health. Research shows that adults who consistently sleep fewer than six hours per night are at greater risk of hypertension, while those sleeping more than nine hours may also experience adverse effects. The key is to strike a balance, with seven to eight hours being the optimal range for most individuals. For instance, one user might notice through their health app that their average sleep duration falls short of recommended levels. By setting nightly reminders and incorporating relaxation routines, they can gradually improve their sleep habits and, consequently, their blood pressure trends.
Tips for Improving Sleep to Support Healthy Blood Pressure
Improving sleep quality begins with creating a consistent bedtime routine. Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps regulate the circadian rhythm, promoting more restorative sleep. Reducing screen time an hour before bed, avoiding caffeine in the late afternoon, and engaging in calming activities like reading or meditation also contribute to better sleep. Additionally, wearable health devices paired with apps can provide valuable insights into sleep patterns, enabling users to make data-driven adjustments. For example, one individual noticed frequent restlessness through their app and adopted a pre-sleep stretching routine, leading to marked improvements in their sleep quality and blood pressure stability. Finally, monitoring blood pressure at optimal times, such as in the morning or evening, offers a clearer understanding of how sleep impacts cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Quality sleep is a cornerstone of maintaining healthy blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health. By understanding how sleep regulates blood pressure, addressing issues like poor sleep or disorders, and leveraging modern tools like health apps and wearable devices, individuals can take control of their health. Prioritizing sleep isn’t just about feeling rested—it’s a vital step toward a longer, healthier life. Start making small changes today, and let restful nights pave the way for better heart health tomorrow.





