Sleeve Bearing vs Ball Bearing – Which is Better?
When it comes to machines and moving parts, choosing the right bearing can make everything run smoothly—or cause problems if you choose the wrong one. Sleeve and ball bearings both help machines spin, but work differently and suit different needs.
This blog post compares sleeve bearing vs ball bearing, explaining how they work, their pros and cons, and the best places to use each one. It’s a helpful guide for engineers and anyone curious about how machines run smoothly.
What Are Sleeve Bearings?
Sleeve bearings (also called plain bearings or bushings) are simple hollow cylinders that let shafts slide or rotate smoothly with less friction. Unlike ball bearings, they work by sliding, not rolling.
How They Work
A thin layer of oil or grease keeps the shaft and sleeve from rubbing directly, which reduces friction and wear. Some sleeve bearings have small grooves or holes that hold the oil better, so they work longer and smoother.
Materials Used
- Bronze: strong and wear-resistant, good for heavy loads
- Steel: durable and tough
- Stainless steel: rust-resistant, ideal for harsh conditions
- Plastic composites (like PTFE): light, corrosion-resistant, sometimes self-lubricating
Common Uses
Found in cars (seat adjustments, steering), industrial machines (pivot points), electronics (quiet fans), and marine equipment (water-exposed parts). Sleeve bearings are simple, reliable, and affordable parts that reduce friction and support moving parts in many machines.
See also: Netflix Grand Autodixitengadget
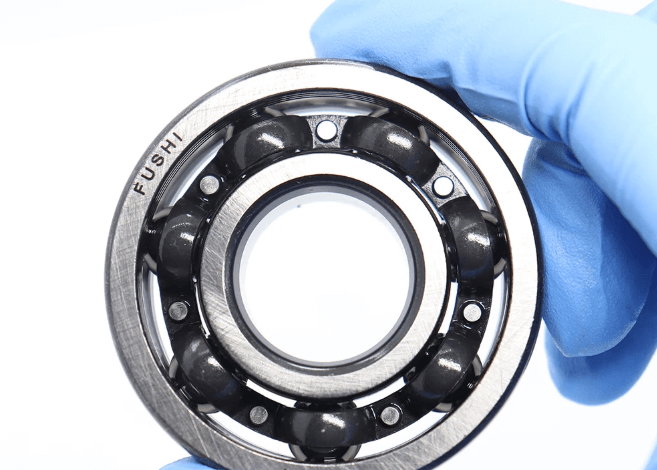
What Are Ball Bearings?
Ball bearings reduce friction between rotating parts using four main components: an inner ring (that fits the shaft), an outer ring (fixed around the shaft), rolling balls between the rings, and a cage that keeps the balls evenly spaced. They support forces acting sideways (radial) and along the shaft (axial).
How They Work
The balls roll between the rings instead of sliding, greatly reducing friction. The cage keeps the balls evenly spaced to ensure smooth and consistent operation.
Materials Used
- Chrome steel: hard and durable, most common
- Stainless steel: rust-resistant, good for wet or corrosive environments
- Ceramics (e.g., silicon nitride): ideal for high speeds and temperatures, corrosion-resistant
- Plastic composites: lightweight and corrosion-resistant, for special needs
Common Uses
Found in cars (engines, wheels), industrial machines (pumps, conveyors), electronics (hard drives, fans), and aerospace (jet engines). They are ideal for fast-spinning, precise, and versatile applications. Ball bearings are essential parts that reduce friction and support loads in many machines, improving performance and durability.
Key Differences Between Sleeve Bearings and Ball Bearings
Choosing the right bearing matters for getting the best performance, lasting longer, and saving money. Here’s how sleeve bearings and ball bearings compare:
1. Design & How They Work
- Sleeve Bearings: A simple cylindrical sleeve lets the shaft slide inside, separated by a thin layer of lubricant. They reduce friction through sliding.
- Ball Bearings: Small round balls roll between two rings (inner and outer), greatly reducing friction and allowing the bearing to handle forces from different directions.
2. Performance & Durability
- Sleeve Bearings: Sleeve bearings are usually quieter and cheaper at low speeds but wear out faster, especially under high speed or heat, due to sliding friction and lubricant breakdown.
- Ball Bearings: Last longer and work well at high speeds and temperatures. They are tougher for heavy or precise tasks, but can be noisier and cost more.
3. Cost & Maintenance
- Sleeve Bearings: Cost less at first, but need more frequent upkeep and may need to be replaced sooner, which can add up.
- Ball Bearings: More expensive initially, but usually need less maintenance, saving money over time, especially for demanding uses.
4. Where to Use Them
- Sleeve Bearings: Best for low to moderate speeds and lighter loads — think small motors, household appliances, and mostly horizontal setups.
- Ball Bearings: Ideal for high speed, heavy loads, or precise movements, like in industrial machines, cars, and computer fans. They work well in any orientation.
Use sleeve bearings if you want a cost-effective, quiet solution for slower, lighter tasks with simple maintenance. Choose ball bearings when you need strong, durable, and efficient performance for fast, heavy-duty, or precise machines.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sleeve Bearings
Sleeve bearings (also called plain or journal bearings) are simple parts that help reduce friction between a spinning shaft and its housing.
Advantages
- Low-cost and budget-friendly.
- Quiet operation—ideal for noise-sensitive areas.
- Simple design for easy installation and maintenance.
- Absorb vibration for smoother machine performance.
- Compact, yet can handle heavy loads in small spaces.
Disadvantages
- Limited to low speeds and lighter loads.
- Require consistent lubrication to avoid wear.
- It must be installed correctly to work well.
- Wear out faster with continuous use.
Sleeve bearings are ideal for quiet, slow machines on a budget. Proper lubrication and installation help them perform well and last longer.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ball Bearings
Ball bearings are common parts used in many machines because they help things move smoothly and efficiently. Here’s a simple overview of their main pros and cons:
Advantages
- Reduce friction for smooth and cool operation.
- Works well at high speeds.
- Handle both side (radial) and front/back (axial) forces.
- Affordable and widely available.
Disadvantages
- Not ideal for very heavy loads due to point contact.
- Sensitive to misalignment, which can cause wear or failure.
- Can produce noise and vibration at high speeds or if misaligned.
- Prone to damage under extreme pressure.
Ball bearings are excellent for smooth, fast, and versatile use but require careful handling of load, alignment, and noise to ensure long life and good performance.
Choosing Between Sleeve Bearings and Ball Bearings
Choosing the right bearing depends on what your machine needs. Here’s a simple guide to help you decide:
Sleeve Bearings
Best For:
- Slow and Light Use: Great for machines that move slowly and carry light loads.
- Saving Money: Usually cheaper upfront, good if you have a tight budget.
- Quiet Operation: They make less noise, which is good for quiet environments.
Things to Keep in Mind:
- Needs More Maintenance: They can wear out faster and need regular care.
- Regular Lubrication: They must be kept well-lubricated to work properly.
Ball Bearings
Best For:
- Fast and Heavy Use: Built to handle fast spinning and heavier weights well.
- Lasting Longer: With proper care, they usually last longer.
- Flexible Use: Works well in many types of machines and industries.
Things to Keep in Mind:
- Cost More: Usually more expensive than sleeve bearings.
- Can Be Noisy: Might make noise, especially when spinning fast.
How to Decide
- Check Speed and Load: Think about how fast the machine moves and how much weight it carries.
- Consider the Environment: Look at the temperature, moisture, and dirt your machine will face.
- Budget: Weigh the initial price against how much maintenance and replacement will cost over time.
- Space: Make sure the bearing fits the space you have available.
With these factors, you can choose the right bearing for your machine, so it runs smoothly and lasts a long time.





